Group Selection and Game Theory
The term “survival of the fittest” represents one of the basic fundamentals of the way of life in nature. In any species, the organisms that holds the weakest traits will be wiped out from its population due to natural selection while only the strongest and smartest animals survive. As a result, there many of the strongest organisms choose to act selfishly in order to benefit their own well-being. However, even though natural selection is determined by the survival of the fittest, there are many situations nature in which organisms pursue altruistic practices over selfish ones.
Computer scientist William Press and physicist Freeman Dyson wrote a paper that explained how organisms are able to act selflessly while maximizing their own chance of survival as well as their entire community. This type of behavior exists across all types of organisms, such as bats, monkey, and even bacteria.
An interesting example of such altruistic behavior can be observed in many species of monkeys. When a predator is near, a monkey can choose to quietly run away from danger or let out a warning call to alarm the other monkeys. However, by doing so, the monkey endangers itself by exposing itself to the predator. As releasing an alarm call decreases its chance of survival from the predator, why would the monkey risk its life for others?
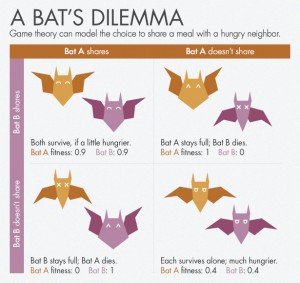
As taught in lecture, in a simple prisoner’s dilemma scenario, the easy choice would be to defect, or run away in the case of the monkey. However, the idea of group selection results to a different type of behavior as the prisoner’s dilemma scenario only takes into account one event. Since encountering a predator will happen many times in a monkey’s lifetime, it is actually more beneficial a monkey to warn its neighbors and they return the favor. As a result, in large groups, cooperative organisms are more likely to survive than uncooperative ones since individuals are able to benefit from the reciprocation of others. This strategy is consistent for many situations, such as why bats share blood and food and how birds take turns taking the lead in V-formation during migration journeys.
As we have learned in lecture that the idea of game theory can be applied to simple case such as prisoner’s dilemma, there are many situations that draw a much more complex analysis in the field of game theory.
Source: https://www.quantamagazine.org/20150212-game-theory-calls-cooperation-into-question/