Learning never exhausts the mind. -Leonardo da Vinci
One of the key tenants of IPM is knowing your pests, or potential pests, and risks. Learning opportunities become a valuable tool in helping to prepare for and prevent pest issues from arising. Here are some upcoming opportunities, most of them free.
NYS IPM Program
The NYS IPM Program partners with local organizations to provide a variety of educational opportunities. Here are a few to check out.

NYS IPM will be at Insectapalooza talking ticks. Learn how to find them and leave with a tick removal kit.
October 19, 2019
Okay, not directly school or child care related, but fun! NYS IPM will be at the Cornell Department of Entomology’s Insectapalooza which promises to be “bigger and buggier” than ever. Pick up some ideas for bringing entomological adventures into the classroom. We heard rumors about chocolate covered crickets.
October 31, 2019
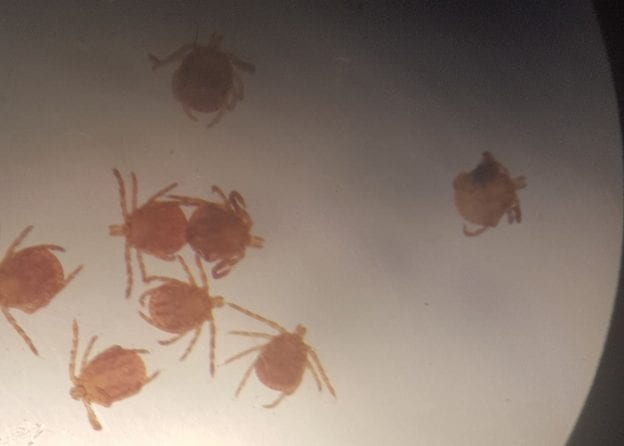
Just in time for Halloween, join NYS IPM’s Jody Gangloff-Kaufmann and Joellen Lampman to cover the scary topic of ticks on school grounds. Sponsored by NYSIR, the Tick Awareness & Management Workshop for Schools will take place in Saratoga Springs. This three hour workshop includes information on ticks and participants will build their own tick drags. We’ll then go outside to look for ticks on the school grounds. The event is free, but registration is required.
November 21, 2019
Capital Region BOCES is hosting Pest Management for Today’s Schools. We’ll discuss NYS regulations, turf and grounds IPM, and structural IPM. A walk-through exercise will be conducted at the end of the session to demonstrate pertinent IPM topics. The workshop is FREE for staff and administrators from districts participating in the BOCES Health-Safety-Risk Service and $25 for staff and administrators from non-participating districts and municipalities. A continental breakfast and lunch is included. Please register for the workshop by November 14, 2019.
April 22, 2020
Every year the NYS IPM program hosts an annual conference. The 2020 conference will focus on school IPM and be held in the NYSUT facility in Latham, NY. Save the date!
For more NYS IPM Program events, visit the New York State Integrated Pest Management Program Facebook events page.
EPA Webinars
For additional opportunities, the EPA hosts a webinar series featuring national experts from across the country, many of which directly address schools and child care centers. Upcoming relevant webinars include:
October 24, 2019 Preventing and Controlling Stored Product Pests
November 7, 2019 Smell That? IPM for Stink Bugs in Homes and Other Structures
December 10, 2019 IPM in Child Care Centers
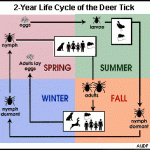
February 2020 New Tick Threats and Controls – A Panel Discussion
March 2020 Creating Monarch Habitats in Schools and Communities
Previous events covered a variety of topics including IPM 101, IPM resources, bed bugs, head lice, turf grass, cockroaches, ants, ticks, mosquitoes, stinging insects, rodents, and birds. Webinar PDFs are available for all presentations and the recorded webinar is available for many.
Continuous Information
The Pest Defense for Healthy Schools
The NYS IPM Schools and Daycare Centers webpage has a number of resources to help your facility provide a safe learning environment.
The Pest Defense for Healthy Schools, formerly known as Stop School Pests, is an online, school health training course for K-12 employees to improve school health. Users can choose from nine online courses, each created for different school staff groups.
NYS IPM Program Web Resources
And, of course, the NYS IPM Schools and Daycare Centers webpage is always available at https://nysipm.cornell.edu/community/schools-and-daycare-centers/.