The time of the falling leaves has come again. Once more in our morning walk we tread upon carpets of gold and crimson, of brown and bronze, woven by the winds or the rains out of these delicate textures while we slept. – John Burroughs, The Falling Leaves
A recent study, Artificial Accumulation of Leaf Litter in Forest Edges on Residential Properties via Leaf Blowing Is Associated with Increased Numbers of Host-Seeking Ixodes scapularis Nymphs published in the Journal of Medical Entomology, showed that areas where leaves were raked or blown into forest margins tripled the number of blacklegged tick nymphs compared to areas where leaves were not artificially accumulated. (There was no observed impact on lone star ticks.)
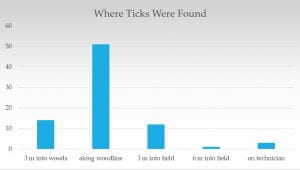
Combine this with the findings of a Cornell study, Active surveillance of pathogens from ticks collected in New York State suburban parks and schoolyards, and it is clear that woodland edges are the areas of highest risk for students to encounter ticks. Fortunately, most students don’t spend much time in these areas. Unfortunately, students will chase stray balls into these areas when ticks are furthest from their minds.
 What can you do to protect students from these tick risky areas? Step one would be to monitor your school grounds for ticks. This low tech monitoring technique can easily be accomplished by a coach, playground monitor, or even students. Knowing that ticks are active can allow for some adjustment of play, like putting up cones to let students know areas are off limits.
What can you do to protect students from these tick risky areas? Step one would be to monitor your school grounds for ticks. This low tech monitoring technique can easily be accomplished by a coach, playground monitor, or even students. Knowing that ticks are active can allow for some adjustment of play, like putting up cones to let students know areas are off limits.
Is there an area with consistently high tick activity? Installing fences or netting can prevent stray balls from entering wooded edges. Think of it as reverse exclusion – in this case, we’re keeping the students out of the pest areas.
Keep in mind that blacklegged ticks prefer high humidity, so look to reduce shady and damp areas where students spend time. We can modify parts of the school grounds to make them less hospitable to ticks by:
- Removing leaf litter from wooded edges in high traffic areas
- Removing trees shading play areas if monitoring shows those areas have tick activity
- Replacing wood mulch, which can store moisture, if monitoring shows tick activity, with a different, drier option
- Widening trails to reduce the risk of students brushing against vegetation
- Eradicating invasive plants, such as Japanese barberry, honeysuckle, and multiflora rose, that easily establish along wooded edges, and have been associated with higher concentrations of ticks carrying disease-causing pathogens
For more information on ticks and schools, check out our updated fact sheet Understanding and Managing Ticks – A Guide for Schools, Child Care and Camps. Additional information can be found on our website Don’t Get Ticked NY.