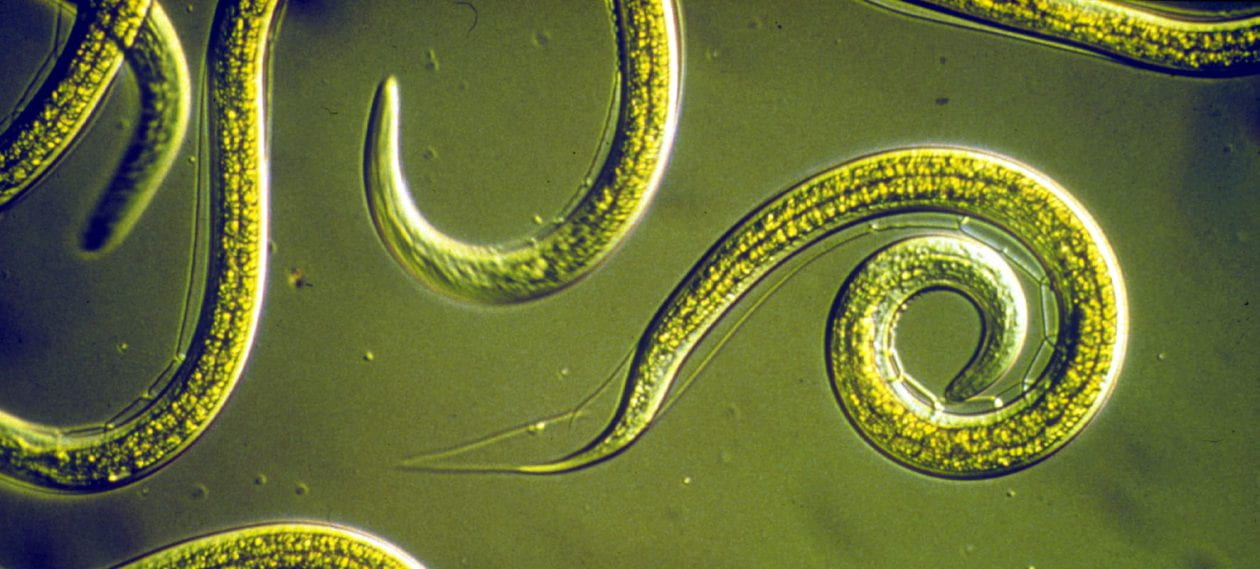
One of the most difficult things for me to deal with as an organic gardener is how to control insect pests in my garden and small orchard. There are times that none of the organic controls that I implement do a very good job in controlling insect damage. The two insect culprits I find the most difficult to control are striped cucumber beetles and squash vine borers, both of which feed on plants in the curcurbit family which includes squash, melons, pumpkins, and zucchini. I’d like to share a bit more about these insects and then about how I’m using beneficial nematodes to control their population in my garden.
Cucumber beetles have evolved to perfectly time their emergence from the soil to coincide with the time cucumber seeds germinate and pop out of the ground. The first generation of beetles overwinter in the soil, undergo pupation, and then emerge as adults. Their first order of business is to attack the new cucumber plant’s first two leaves (called cotyledons) and then any new leaves and stems that have grown. Adult feeding can set back plant growth and may at times even kill the plant altogether. Adult beetles will then breed and females lay their eggs on the soil at the base of the plant. Eggs hatch in a few weeks and larvae burrow into the soil to begin feeding on roots and parts of the plant stem underground.
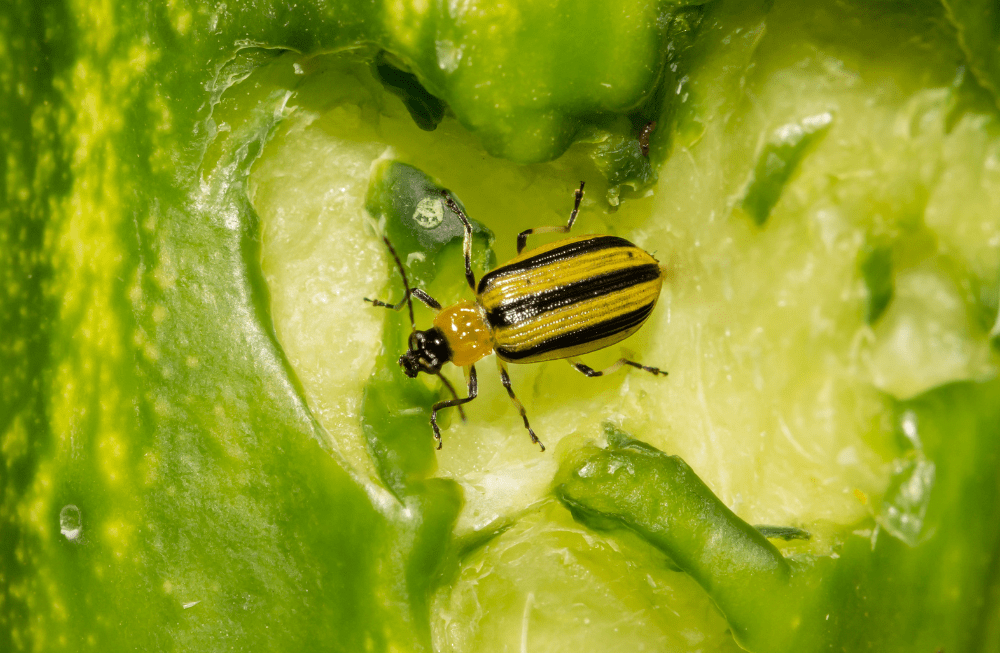

And that’s just the first generation of beetles! If you’re lucky enough that your plants survive the initial round of attack and are thriving under the June sun, a second generation of beetle larvae are busily consuming roots and maturing in the soil. About 40 days after hatching, the new brood of adult beetles will emerge to feed heavily on the flowers, leaves, and vines of your plants. This second generation of beetles will not only set back plant growth and fruiting, but may also introduce bacterial wilt into the plants. Bacterial wilt closes off the transport of water up the stems and to the developing fruit, causing the plant to wilt and die over just a few days. Eggs are again laid on the soil surface, they hatch, and larvae dig into the soil looking for roots to feed on. These larvae will overwinter in the soil to emerge the following spring as adults. Read more Beneficial Nematodes: Holy Grail of Organic Pest Control?