Contents
View from the Field
Potato Leafhopper
Be on the lookout for potato leafhopper (PLH) in alfalfa. There were no fields listed over threshold this week but crop consultants are finding PLH in alfalfa. It is best to start scouting now to monitor the increase of the population over the summer. When fields start having potato leafhopper nymphs with warm weather is when there is potential for damage. Be ahead of the population and avoid damage my scouting. For more information on thresholds and management, view the following video:
IPM for Potato Leafhopper on Alfalfa
Alfalfa Weevil Alert!
There are reports of many alfalfa fields being over threshold for alfalfa weevil this week.
The good thing is that they will pupate soon and not be an issue. The threshold for alfalfa weevil in regrowth is: “After harvest, check stubble and regrowth for signs of weevil feeding. If 50 percent of regrowth shows signs of weevil feeding, larvae are <3/8 inch long, and there are few or no weevil cocoons, the field may need to be treated with an insecticide.” (https://fieldcrops.cals.cornell.edu/forages/insects-forage-crops/alfalfa-weevil/)
Alfalfa weevil damage
Corn Rootworm
Have you seen fireflies around your fields? The thing is when you start to see fire flies is about the same time as when corn rootworm hatches from eggs in the soil and starts feeding on corn. IPM for Corn Rootworm in Field Corn
Black Cutworm
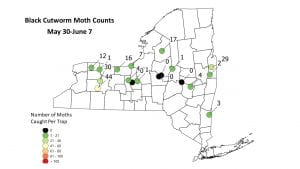
There are a few reports of black cutworm being over threshold in Western NY. Not everyone has reported for last week but the ones that have had low-flight moth catches.
NYS IPM Black Cutworm Short Video
Black Cutworm and Damage to Corn
Cereal Leaf Beetle
If you have a field with cereal leaf beetle we would like to sample the larvae for a biocontrol project. Please email me at klw24@cornell.edu
For more information on IPM insect pests of small grain view the following video:
IPM for Insect Pests of Small Grains
Black Cutworm Moth Capture Map
True Armyworm Moth Capture Map
Black Cutworm Degree-Days by Location of Intense Catches
6/14/2021
True Armyworm Moth Captures by Location
6/15/2021
Degree Day Models for Alfalfa Weevil -6/14/2021
Clipboard Checklist
Keith Waldron, NYS IPM
General
*Walk fields to check tile flow, check and clear drainage outlets. Look for line breaks
*Note and record location of wet areas on field maps or aerial photo for future tiling considerations and crop decisions, check for areas of soil erosion
*Pre-plant weed evaluation, timing cultivation and/or pre-plant weed management
*Watch for early season weeds: winter annuals, chickweed, henbit, field penny cress, shepherd’s purse, giant and common ragweed, purple deadnettle, lambsquarters, redroot pigweed, velvet leaf, Pennsylvania smartweed, common sunflower, quackgrass, foxtail
Alfalfa:
*Evaluate established legume stands for winter damage (thinning stand, frost heave, Brown root rot), determine average alfalfa stand count adjust crop plans if necessary
*Monitor for alfalfa weevil, crown or foliar diseases
*Monitor new seedings for Pythium blight and Phytopthora Root Rot.
*Monitor for Alfalfa Snout Beetle (In Oswego, Jefferson, Cayuga, Wayne, Lewis, St. Lawrence, Clinton, Essex, and Franklin counties)
Small Grains:
*Monitor winter grain fields for over wintering survival (snow mold and other cold injury issues), weed issues (such, as winter annuals, corn chamomile and chickweed), growth stage, number of tillers, foliar diseases (powdery mildew, rusts)
*Check stands for soilborne virus diseases, Wheat spindle streak mosaic and Soilborne wheat mosaic, check for signs of powdery mildew or other maladies, cereal leaf beetle, weed escapes, goose damage
Corn:
*Prepare land and plant corn as conditions allow
*Pre-plant weed evaluation, timing cultivation and/or pre-plant weed management
*Emergence: assess stand, population count
Soybeans:
*Prepare land and plant soybeans as conditions allow
*Pre-plant weed evaluation, timing cultivation and/or pre-plant weed management
Pastures:
*Check and mend fences as needed.
*Check crop growth
*Monitor fields for invasive species, plants harmful to livestock
*Review/Plan rotation system
Equipment:
*Remove / clean soil and crop debris from equipment
*Arrange for custom weed control or check your own application or cultivator equipment for repairs.
*Carry appropriate / necessary NYS DEC and EPA required documents: (pesticide applicators license, pesticide labels, MSDS sheets, etc.) with application equipment
*Calibrate:
-planting equipment – maintain records on planting rate per field
-manure spreaders – maintain records on amount spread per field
-pesticide application equipment – Check nozzles, pumps, etc., recalibrate pesticide application equipment before use.
Storage:
* Check stored grain bins for temperature, moisture and signs of mold and insects. Aerate, core, transfer grain or treat as necessary
*Check forage allocation and anticipate feed program adjustments as forages from previous year are used up
*Plan where forages should be stored for optimum allocation next feeding season