fsttopsort topologically sorts its input if acyclic, modifying it. Otherwise, the input is unchanged. When sorted, all transitions are from lower to higher state IDs. (documentation source)
Cyclic Example:
fstprint –isymbols=words.txt –osymbols=words.txt L1.fst
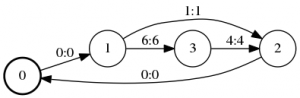
0 1 <eps> <eps>
1 2 a a
1 3 f f
2 0 <eps> <eps>
3 2 d d
when we apply fsttopsort, we get a warning saying “input FST is cyclic”.
fsttopsort L1.fst L1sorted.fst
WARNING: fsttopsort: Input FST is cyclic
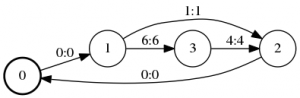
fstprint –isymbols=words.txt –osymbols=words.txt L1sorted.fst0 1 <eps> <eps>
1 2 a a
1 3 f f
2 0 <eps> <eps>
3 2 d d
As we expected, the output looks unchanged.
Acyclic Example:
fstprint –isymbols=words.txt –osymbols=words.txt L2.fst
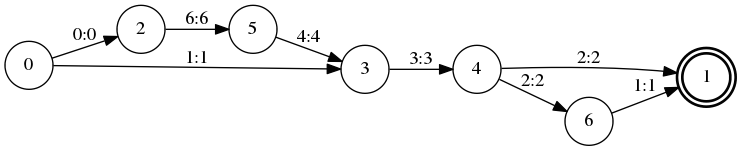
1
0 2 <eps> <eps>
0 3 a a
2 5 f f
3 4 c c
4 6 b b
4 1 b b
5 3 d d
6 1 a a
as we run the operation,
fsttopsort L2.fst L2sorted.fst
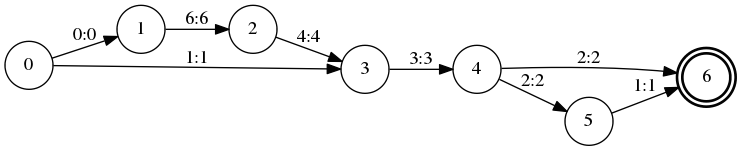
fstprint –isymbols=words.txt –osymbols=words.txt L2sorted.fst6
0 1 <eps> <eps>
0 3 a a
1 2 f f
2 3 d d
3 4 c c
4 5 b b
4 6 b b
5 6 a a
we can see the state IDs topologically sorted.
(I produced all the images by running ‘fstdraw [fst filename] | dot -Tpng >[png filename]’)