Electrophoresis, 2004: Zeta potential of microfluidic substrates: 2. Data for polymers
Citation: Brian J. Kirby, Ernest F. Hasselbrink Jr., Zeta potential of microfluidic substrates: 2. Data for polymers, Electrophoresis, 25, 203–21, 2004 doi pdf
Abstract: Zeta potential data are reviewed for a variety of polymeric microfluidic substrate materials.
Many of these materials currently used for microchip fabrication have only recently
been employed for generation of electroosmotic flow. Despite their recent history,
polymeric microfluidic substrates are currently used extensively for microchip
separations and other techniques, and understanding of the surface z potential is
crucial for experimental design. This paper proposes the use of pC (the negative
logarithm of the counterion concentration) as a useful normalization for the z potential
on polymer substrates in contact with indifferent univalent counterions. Normalizing
z by pC facilitates comparison of results from many investigators. The sparseness of
available data for polymeric substrates prevents complete and rigorous justification
for this normalization; however, it is consistent with double layer and adsorption
theory. For buffers with indifferent univalent cations, normalization with the logarithm
of the counterion concentration in general collapses data onto a single z/pC vs. pH
curve, and (with the exception of PMMA) the repeatability of the data is quite
encouraging. Normalization techniques should allow improved ability to predict z
potential performance on microfluidic substrates and compare results observed
with different parameters.
Figures:
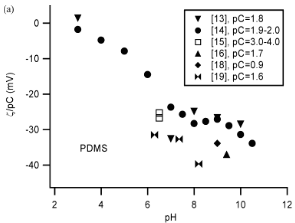
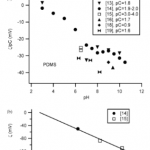
- Figure 1. (a) z /pC vs. pH for PDMS. (b) z vs. pC for PDMS (6.5 , pH , 7). For this and all of the following figures, closed symbols denote electroosmotic or electrophoretic measurements, open symbols denote streaming current or streaming potential measurements.
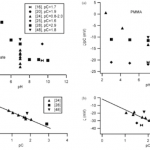
- Figure 2. (a) z/pC vs. pH for polycarbonate. (b) z vs. pC for polycarbonate (6.8 , pH , 7.2). Linear fit is to data of [24]. Figure 3. (a) z/pC vs. pH for PMMA. (b) z vs. pC for PMMA (7 , pH , 8). Linear fit is to data of [31].
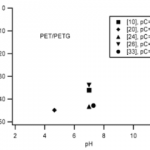
- Figure 4. z/pC vs. pH for PET/PETG.
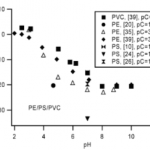
- Figure 5. z/pC vs. pH for PE/PS/PVC.
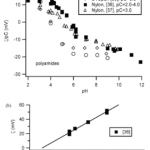
- Figure 6. (a) z/pC vs. pH for polyamides. (b) z vs. pC for nylon (4 , pH , 4.5).
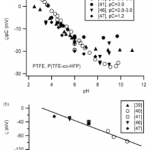
- Figure 7. (a) z/pC vs. pH for perfluoropolymers. (b) z vs. pC for PTFE (5.5 , pH , 6). [40, 41] used plasma-deposited or treated PTFE; others used PTFE or P(TFE-co-HFP) capillaries (HFP, heafluoropropylene.