Applied Optics, 2001: CO2 imaging with saturated planar laser-induced vibrational fluorescence
Citation:
Kirby BJ, Hanson RK, CO2 imaging with saturated planar laser-induced vibrational fluorescence, Applied Optics, 40:6136-6144 (2001). doi pdf
Abstract:
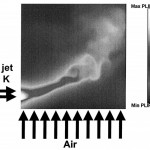
We present new vibrational infrared planar laser-induced fluorescence PLIF imaging techniques for CO2 that use a simple, inexpensive, high-pulse-energy transversely excited atmospheric CO2 laser to saturate a CO2 absorption transition at 10.6 micron. Strong excitation by use of a CO2 laser provides increased signal levels at flame temperatures and simplifies image interpretation. Because rotational energy transfer and intramodal vibrational energy transfer are fast, vibrational distributions can be approximated by use of a simple three-temperature model. Imaging results from a 425 K unsteady transverse CO2 jet and a laminar coflowing CO-H2 diffusion flame with temperatures near 1500 K are presented. If needed, temperature-insensitive signal levels can be generated with a two-laser technique. These results illustrate the potential for saturated infrared PLIF in a variety of flows.
Figures:
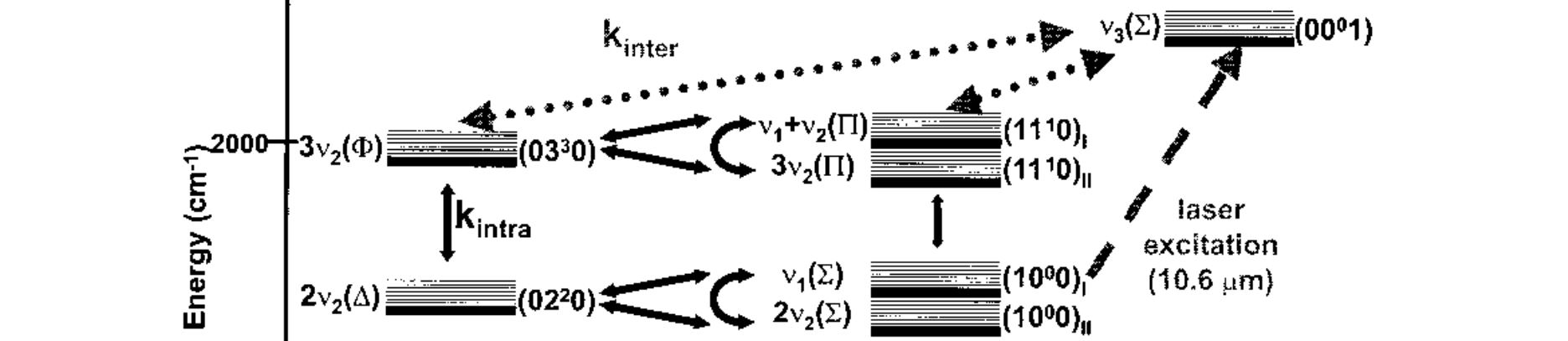
- Fig. 1. Vibrational manifold showing energy-transfer processes for CO2 during and after laser excitation at 10.6 microns. doi pdf
- Fig. 3. Predictions of the three-temperature model for the laser-pumped mode temperature and the fluorescence yield as a function of initial temperature. doi pdf
- Fig. 4. Comparison of LIF signal levels at a constant CO2 mole fraction as predicted by the three-temperature model and a detailed rate-equation model. doi pdf
- Fig. 5. IR LIF signal normalized by CO2 mole fraction for saturated excitation of CO2. Effect of a) CO2 and b) H2O mole fractions. doi pdf
- Fig. 8. CO2 IR PLIF imaging in a CO/H2 flame. a) Flame schematic, b) single-shot image, c) 36-frame average. Images are cropped horizontally. doi pdf
- Fig. 9. Combined OPO-CO2 laser excitation scheme. a) Excitation steps shown on an energy-level diagram, b) excitation steps shown on a timing diagram. doi pdf
- Fig. 10. LIF signal at constant CO2 mole fraction as a function of temperature for two excitation schemes. doi pdf