I have a long-standing interest in the neural circuitry involved in instrumental learning dating back to graduate school. Interestingly, many of these ideas carry through to our current understanding of the role of the retropslenial cortex (see Smith et al., 2018). For example, auditory discrimination learning depends on an extended limbic circuitry which includes the hippocampus, amygdala, anterior and posterior cingulate/retrosplenial cortex, auditory cortex and several thalamic nuclei.
Within this broad ‘limbic learning circuit’, different sub-circuits make different contributions to the learning process. For example, circuitry involving the posterior cingulate cortex and the anterior thalamus is involved in encoding stimuli that reliably predict reinforcement or the need for a behavioral response. Circuitry involving the anterior cingulate cortex, amygdala and medial dorsal thalamus is involved in promoting attention to behaviorally relevant cues, especially those cues that predict highly arousing reinforcement such as a reward or punishment.
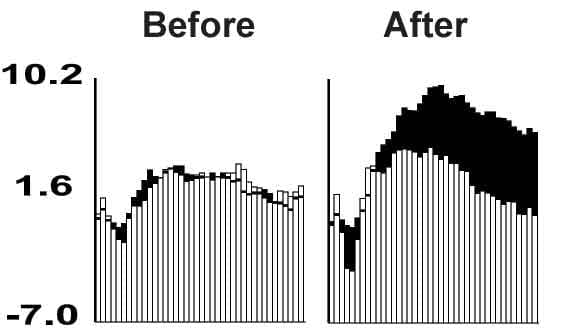
Figure.
During learning, neurons in the cingulate/retrosplenial cortex become more responsive to an auditory tone that predicts reinforcement (black bars) than to a tone that does not predict reinforcement.
Smith, D. M., Freeman, J. H., Jr., Nicholson, D., & Gabriel, M. (2002). Limbic thalamic lesions, appetitively motivated discrimination learning, and training-induced neuronal activity in rabbits. The Journal of Neuroscience, 22(18), 8212–8221. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.22-18-08212.2002 ![]()
Smith, D. M., Monteverde, J., Schwartz, E., Freeman, J. H., Jr., & Gabriel, M. (2001). Lesions in the central nucleus of the amygdala: Discriminative avoidance learning, discriminative approach learning, and cingulothalamic training-induced neuronal activity. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 76(3), 403–425. https://doi.org/10.1006/nlme.2001.4019 ![]()
Duvel, A. D., Smith, D. M., Talk, A., & Gabriel, M. (2001). Medial geniculate, amygdalar and cingulate cortical training-induced neuronal activity during discriminative avoidance learning in rabbits with auditory cortical lesions. The Journal of Neuroscience, 21(9), 3271–3281. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.21-09-03271.2001 ![]()