1. Industry Overview:
In France, one of the most popular transport modes is train. SNCF is France’s national railway, providing high speed, overnight and local services in France and beyond into Spain, Switzerland and Italy.
>> http://www.tgv-europe.com/en
Types of Train in France:
Railway industry is quite similar to airline industry, as it sells seats for a transport from an origin to a destination. The price depends on journey, class, and date of booking. Thus, railway industry can be placed in Quadrant 2, where its service has variable prices for a predictable duration. This industry also has the appropriate characteristics to apply revenue management strategies. Those characteristics are:
– Inflexible capacity: the number of seats on a train is fixed
– Variable and uncertain demand: the demand is different depending on the time of day, day of week, origin-destination pairs, and purpose of travel
– Perishable inventory: the unoccupied seat cannot be inventoried, and the revenue of that seat is missed
– Low marginal cost and high production cost
– Product can be sold in advance
– Heterogeneous customers with different segments, varying by age, purpose of travel, independent or group, etc.
However, there are some differences that make the revenue management of railway industry is little bit different than that of airline industry.
– More difficult to forecast demand and to have the accurate number of travelers on a service: no check-in procedure, open tickets (rail pass) generally allow passengers to travel on any rail service, walk up tickets are very common (a large number of passengers purchase their tickets on the day from the station)
– Less difficult to deal with overbooking: passengers are often allowed to stand during train journeys hence increasing capacity beyond the number of seats
———
2. Space
Railway industry defines space implicitly.
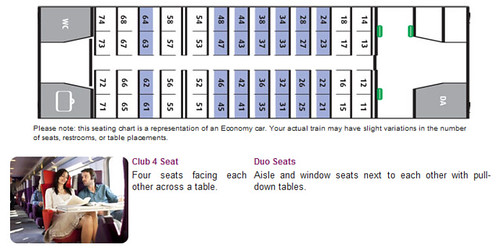
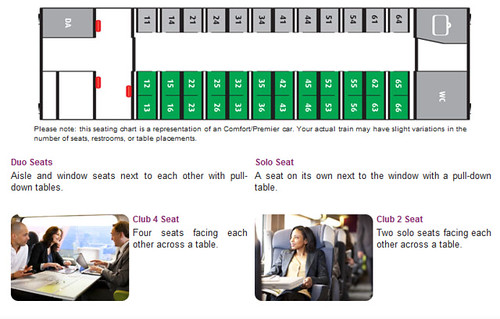
Normally, a train has two classes: Economy (2nd Class) and Comfort (1st Class). The seating options and services are different for each class. The price is same for different seating options in a class.
Trains, especially TGV has “TGV bar”, which provides a wide selection of meals and sweet snacks available for purchase. Additionally, the TGV bar offers films on DVD, magazines, games for children, Paris Metro tickets, even USB sticks for purchase. There is also a rolling snack cart that comes to the customers’ seats.
For additional revenue, TGV offers Premium service includes 1st Class seat, meal service, and access to the TGV lounge at the train stations.
Personally, I would charge difference fares for different seating options in each class. A group will want to pay more to have a Club 4 seat. A couple will want the Duo seat or Club 2 seat. And an individual traveler will want a solo seat. As the number of seat are fixed, we can charge for each option, rather than a “first comes first served” policy.
I’m also thinking about a mini-cinema on train, especially overnight train. Normally, the overnight train have load factor less than 80%, so the train can use one car to transform into a mini-cinema with a projector and a screen. When the train is busy, the car will be transformed in normal guest car again.
——
3. Time
Railway industry defines time implicitly.
Although the duration of a journey is determined, the railway industry sells a journey rather than specifically selling time. In addition, there may be issues that cause the increase/decrease in duration of the journey.
However, the railway industry also tries to sell time explicitly with the Rail pass. With Rail pass, customers can have unlimited travel on the national rail network of France for a fixed number of days. The choices are 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 or 9-day pass within a one-month period. Travel days may be used consecutively or non-consecutively. Thus, the fare becomes rate-per-day, not anymore rate-per-trip.
>> http://www.raileurope.com/rail-tickets-passes/france-pass/index.html
The industry can sell time explicitly by providing Rail pass with weekly or monthly unit. However, I think it will not be effective as it makes the demand forecasting much more complicated. Half-day unit won’t make sense as a trip is normally more than 3 hours.
——–
4. Price
Tickets can be purchased 60 to 120 days in advance depending on the route.
Ticket discounts are based on advance purchase, availability, and certain restrictions. Everyone is eligible to receive discounted fares by purchasing an Economy or Comfort class ticket in advance. Youth and seniors can enjoy specific discounts as well. Discounted tickets are available for youth (under 26 of age), seniors (age 60 and over) and children (generally ages 4-11) but should be verified with each product.
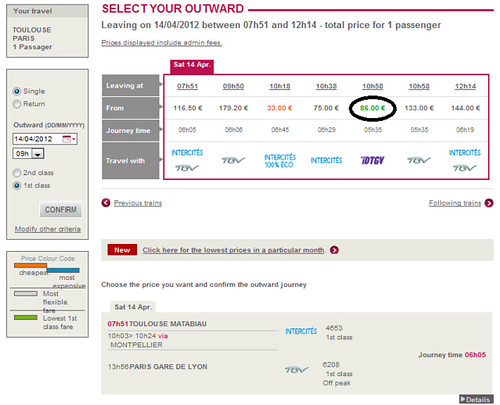
Price at 1 week before departure
Price at 2 weeks before departure
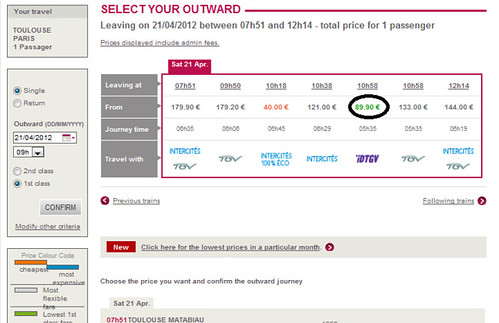
Price at 3 weeks before departure
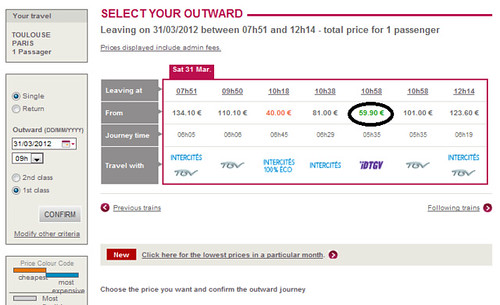
Price at 4 weeks before departure
Normally, prices are reduced for 1or 2 week-advanced purchase, slightly reduced for 3-week-advanced purchased, and stay same for more-than-4-week-advanced purchase.
The physical rate fences are the classes:
The non-physical rate fences are age, season ticket, and loyalty
As the rate fences are now already too sophisticated, I would rather consolidate these fences than create new fences to confuse customers.
(-Thao Ly)
——–
References:
http://www.raileurope.com
http://www.tgv-europe.com
http://www.sncf.co.uk/
Amstrong and Messneir, 2010. Railway revenue management: Overview and Methods
Schroeder, Braun, and Schnieder. Revenue management in the railway industry