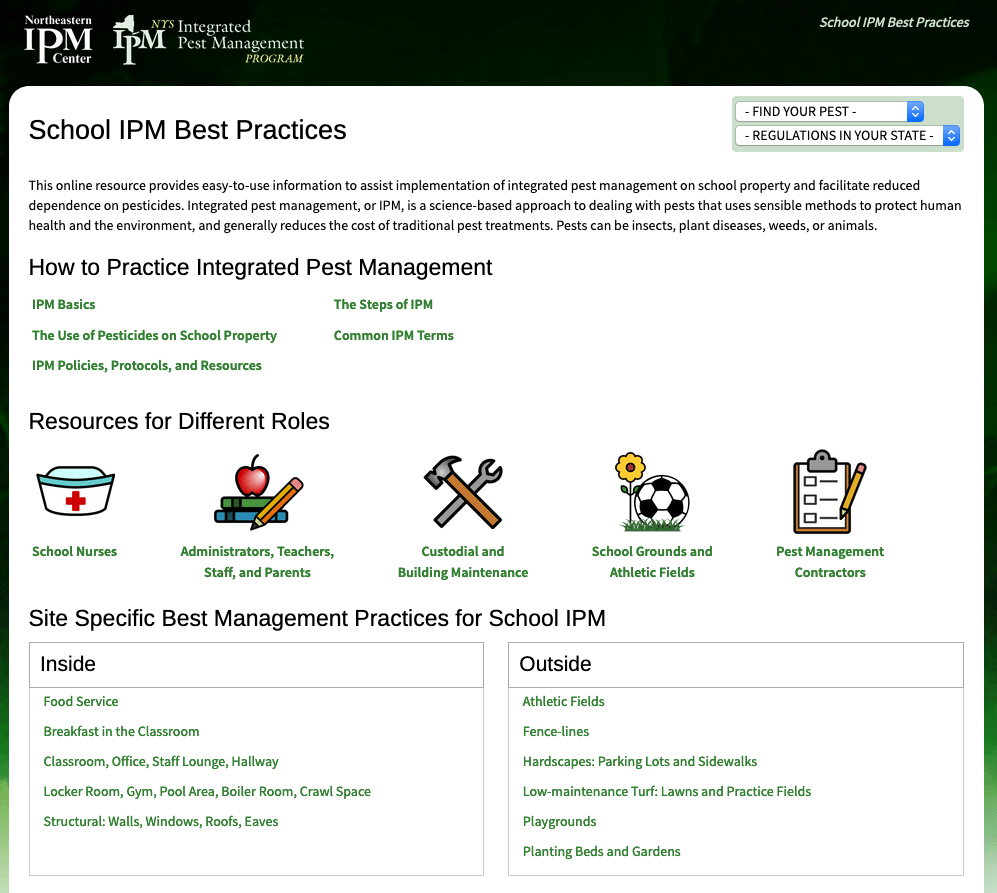
“As everyone knows, when fighting a zombie, you grab a shovel and aim for its head. The same with wild parsnip, except you aim for its feet.” – Paul Hetzler

The bright yellow flowers of wild parsnip can be noticeable from a distance. The sap in this widely spreading invasive plant can cause severe burns.
There is no lack of invasive species in New York – but some do raise more of a concern than others. One such is the wild parsnip. Commonly spotted along roadsides with its bright yellow flowers, it can cause a problem on low maintenance areas on school grounds.
According to the New York Invasive Species Information Clearinghouse, wild parsnip produces furanocoumarin, “a compound in its leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits, that causes intense, localized burning, rash, severe blistering, and discoloration on contact with the skin on sunny days”. Avoid the sap and avoid the chemical burns.
In order to avoid those burns, the NYS DEC recommends:
- Do not touch any parts of the plant with bare skin.
- Wear gloves, long-sleeved shirts, pants, boots and eye protection if working near wild parsnip to prevent skin contact with the sap. Synthetic, water-resistant materials are recommended.
- If contact with sap occurs, wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water, and keep it covered for at least 48 hours to prevent a reaction.
- If a reaction occurs, keep the affected area out of sunlight to prevent further burning or discoloration, and see a physician.
Digging out the root, cutting the root an inch or two below the soil, mowing, and herbicides can all be effective in managing wild parsnip. It is unlikely, however, that an emergency exemption for herbicide use would be approved before seed drop. Mechanical methods will have more long-term benefits.
And wild parsnip is going to seed, so make sure you don’t ensure a new crop next year by spreading seeds around! Before conducting any management, carefully cut the seed heads off with clippers and put them in a plastic bag. The bag can then be left in the sun to rot the seeds before disposal. And don’t forget to wear protective clothing to prevent any sap from reaching exposed skin or eyes.
If you want to learn more about wild parsnip and its management, our favorite guest blogger Paul Hetzler covered it well and humorously in his blog, Vengeful Veggies.
For more pictures of wild parsnip, visit the Turfgrass and Landscape Weed ID website. For information on other invasive species, visit the New York State IPM Program’s Invasive Species page.
And, just in case we didn’t quite get the message across – wear protective clothing and eye wear to prevent sap from causing severe burns.