What is citizen science?
Scientists are limited in the amount of data they can collect by both time and money. With help from members of the general public, known as citizen scientists, researchers are able to crowd source data collection collecting more data from more places helping them find answers to real-world questions.
So if you want to do something fun and educational that contributes to the advancement of scientific knowledge, consider becoming a citizen scientist.
Citizen Science Projects
This project focuses on migration and seasonal changes. People all over the United States, Canada, and Mexico, report sightings of birds, monarchs, frogs, and other organism. Watch as reported sightings are mapped in real-time as waves of migrations that move across the continent.
iNaturalist lets you photograph, identify, and document what’s around you. Every observation can contribute to biodiversity science, from the rarest butterfly to the most common backyard weed. By sharing your observations with scientists, you will help build our understanding of the natural world.
In studying life, scientists have overlooked many regions. Some regions have not been studied because they are so remote. Others because they are so diverse that it is hard to know where to even begin. Then there is the great indoors, which we believe has been understudied in part because it is so immediate. This project aims to document the species that live indoors with humans.
Hundreds of thousands of people around the world contribute bird observations to the Cornell Lab of Ornithology each year, gathering data on a scale once unimaginable. Scientists use these data to reveal how birds are affected by habitat loss, pollution, disease, climate, and other environmental changes. Your participation will help trace bird migration, nesting success, and changes in bird numbers through time.
Celebrate Urban Birds is a citizen science project focused on better understanding the value of green spaces for birds. This project connects people of all ages and backgrounds to birds and the natural world through the arts and fun neighborhood activities.
The goal of this project is to gather this information on bird sightings, archive it, and freely share it to power new data-driven approaches to science, conservation and education. e-Bird also develops tools that make birding more rewarding. It provides the most current and useful information to the birding community from photos and audio recordings, to seeing real-time maps of species distribution and alerts that let you know when species have been seen.
NestWatch is a nationwide monitoring program designed to track status and trends in the reproductive biology of birds, including when nesting occurs, number of eggs laid, how many eggs hatch, and how many hatchlings survive. Their database is intended to be used to study the current condition of breeding bird populations and how they may be changing over time as a result of climate change, habitat degradation and loss, expansion of urban areas, and the introduction of non-native plants and animals.
The Tick App allows people living in high-risk areas for Lyme disease, like Orange County New York, to participate in a tick behavioral study. Participants complete daily logs and report ticks. The app provides information on how to remove ticks, prevent tick bites, and general information about ticks. When enough people are involved, it can also provides information about blacklegged and deer tick activity in our area.
This citizen science project’s mission is to better understand the distribution and abundance of breeding monarchs and to use that knowledge to inform and inspire monarch conservation. People from across the United States and Canada participate in this monarch research. Their observations aid in conserving monarchs and their threatened migratory phenomenon, and advance the understanding of butterfly ecology in general.
Monarch Watch strives to provide the public with information about the biology of monarch butterflies, their spectacular migration, and how to use monarchs to further science education in primary and secondary schools. They engage in research on monarch migration biology and monarch population dynamics to better understand how to conserve the monarch migration.
In the spring and fall volunteers collect observations of adult monarchs. This information is used to assemble quantitative data on monarch numbers at critical times during the breeding season.
Each fall Monarch Watch distributes more than a quarter of a million tags to thousands of volunteers across North America who tag monarchs as they migrate through their area. These citizen scientists capture monarchs throughout the migration season, record the tag code, tag date, gender of the butterfly, and geographic location then tag and release them. At the end of the tagging season, these data are submitted to Monarch Watch and added to their database to be used in research.
In the past twenty years, native ladybugs that were once very common have become extremely rare. During this same time, ladybugs from other parts of the world have greatly increased in both numbers and range. This is happening very quickly and no one knows how, why, or what impact it will have on ladybug diversity. Citizen scientists involved in this project help scientists answer these questions by photographing ladybugs and submitting the photos along with information about when and where the ladybugs were found.
A project of Cornell University’s Garden Based Learning, this web forum provides an avenue for gardeners to share knowledge. Gardeners report what vegetable varieties perform well – and not so well – in their gardens. Other gardeners can view ratings and read the reviews to decide which might work well for them. Researchers use the information gain new insight into the performance of vegetable varieties under a wide range of conditions and practices. The information gathered is also used to make a Selected List of Vegetable Varieties for Gardeners in New York State.
Native pollinators play an essential role in the pollination of flowering plants, including native plants and wildflowers, garden plants, as well as cultivated crops. Some native pollinator species have suffered population declines over the last few decades. Participants in this study submit photographs and/or specimens to help determine the conservation status of a wide array of native insect pollinators in non-agricultural habitats.
iMapInvasives is an on-line, GIS-based data management system used to assist citizen scientists and natural resource professionals working to protect our natural resources from the threat of invasive species. Citizen scientists are provided with resources to help them identify invasive species. Their invasive species findings are aggregated with data from a wide variety of sources contributing to early detection of invasive species as well as analysis of management strategies.
Natural history museums across the world share a common goal – to conserve and make available knowledge about natural and cultural heritage. The Notes from Nature project gives you the opportunity to make a scientifically important contribution towards that goal by transcribing museum records. Every transcription that is completed brings us closer to filling gaps in our knowledge of global biodiversity and natural heritage.
This is an official government website designed to accelerate the use of crowdsourcing and citizen science across the U.S. government. It includes a searchable database of a government-wide listing of citizen science and crowdsourcing projects designed to improve cross-agency collaboration, reveal opportunities for new high-impact projects, and make it easier for volunteers to find out about projects they can join.
Become a Citizen Scientist today!
 Many sources provide great advice on sowing seeds. Key factors include sufficient light and temperature for growing the seeds. But the question inevitably arises when to transplant them outdoors. Don’t rush. Cold soil and air temperatures can stress plants. Wait at least a week or two after the last frost.
Many sources provide great advice on sowing seeds. Key factors include sufficient light and temperature for growing the seeds. But the question inevitably arises when to transplant them outdoors. Don’t rush. Cold soil and air temperatures can stress plants. Wait at least a week or two after the last frost.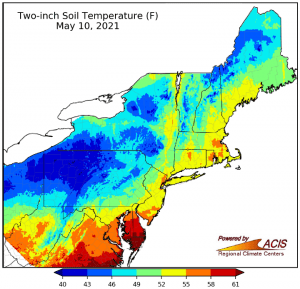 Nighttime temperatures should be consistently above 45°F, and the soil should be warm, about 70°F. You can use black plastic mulch to warm soil and/or row covers, hot caps or other protection to keep plants warm early in the season. Remove covers whenever temperatures exceed 85°F.
Nighttime temperatures should be consistently above 45°F, and the soil should be warm, about 70°F. You can use black plastic mulch to warm soil and/or row covers, hot caps or other protection to keep plants warm early in the season. Remove covers whenever temperatures exceed 85°F. Phenology is a branch of science that studies the relationships such as the life cycles of plants and animals and environmental changes. Seasonal changes such as weather or temperature can be correlated with natural events such as bird migration, plant budding, flowering or fruiting and insect activities. For example, in the Hudson Valley migrating hummingbirds usually arrive when forsythia bloom. Centuries ago, Native Americans began planting corn when oak leaves are the size of a Snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis).
Phenology is a branch of science that studies the relationships such as the life cycles of plants and animals and environmental changes. Seasonal changes such as weather or temperature can be correlated with natural events such as bird migration, plant budding, flowering or fruiting and insect activities. For example, in the Hudson Valley migrating hummingbirds usually arrive when forsythia bloom. Centuries ago, Native Americans began planting corn when oak leaves are the size of a Snowdrop (Galanthus nivalis).













 i-Naturalist
i-Naturalist













