We continue to see increases in BMSB movement to pheromone baited Tedders traps, 50-93% of which are nymph. Traps at three of our monitored sites, Milton-West, Milton-East and Highland have trap captures above 40 per week.
The first adult was found moving to urban structures, seeking overwintering sites. As nymphs mature to adults, increasing numbers will be seeking host food sources to stock up on reserves to take them through 6 months of winter. This ‘feeding frenzy’ often results in very high numbers of BMSB moving to irrigated orchards, especially during dry periods in September and October, if native deciduous tree hosts are unsuitable as a food source.
By far, feeding injury to mid to late season peach appears to be the greatest threat this year. In vegetable sites we are scouting, beans and Jalapeno pepper appear to be favored over tomatoes at this point in time. The pepper damage remains at <1% injury. There are relatively few BMSB in vegetable fields, however, in peach orchards (in Highland), populations feeding on fruit continue to be very high in unsprayed trees. We have seen 5% of our trees with 100% fruit injury with remaining trees with over 20% injury from BMSB feeding. Growers along the Hudson River from Highland to Marlboro should continue intensively scouting along the perimeter of orchards near woodlands or isolated host trees and vegetable sites containing legumes and pepper.
[caption id="attachment_1915" align="alignleft" width="300"]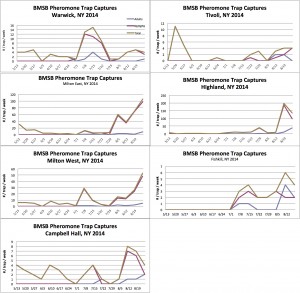 BMSB Pheromone Trap Capture 8.28.14[/caption]
BMSB Pheromone Trap Capture 8.28.14[/caption]
Trap Capture and Scouting Threshold: If BMSB captures exceed 40/ trap per week, or if the insect is observed on the tree, using 1 BMSB per 100 feet of perimeter orchard linear row, applications for management of BMSB should be made. Employ the first available window using one of the most effective insecticides that will best fit your harvest schedule.
The list of the most effective insecticides for BMSB management is found using this link. NYS labeled insecticides effective for use against the BMSB are available in four major classes including pre-mix formulations. Bifenthrin received an emergency exemption use permit (Section 18) to control brown marmorated stink bug (BMSB) on apples, peaches, and nectarines in Orange, Dutchess and Ulster Counties of NY. Products include Bifenthure and Brigade, showing the greatest degree of efficacy of the pyrethroid group. However, bifenthrin has a 30d re-application interval, a 14d PHI and 12h REI.