The Rivalry between Didi and Uber
http://www.breakingviews.com/considered-view/china-taxi-apps-speed-towards-subsidy-showdown/
This article describes the recent heated rivalry between two of the largest ride-hailing apps in China, Didi Kuaidi and Uber. As of June 2015, China’s local company Didi Kuaidi has taken up 99 percent of the ride-hailing market, while the US-based ride-hailing giant Uber has a market valuation of about three times higher than that of its local rival. In order to win the fierce battle and gain dominance in the Chinese market, both firms have adopted price-cutting strategies by heavily subsidizing both drivers and passengers. In order to drive away its competitor, Didi and Uber have both announced plans to invest in up to $2 billion and $1 billion respectively. While this battle is extremely costly, it is believed that once a single firm establishes a dominating position in the market, it should be able to discontinue its subsidies and begin earning profit.
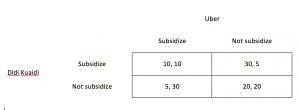
At first glance, one may think that Uber and Didi’s subsidy is simply a marketing decision. However, upon closer inspection, one can actually apply the analysis of Game Theory to each company’s decision to subsidize or not. Consider the case when Didi does not subsidize. In this case, Uber will earn maximum revenue if it subsidizes because existing customers of Didi will likely turn to Uber. Moreover, in the long run, Uber wants to gain dominance in the market and drive away its competitor. As such, it has a strong incentive to provide subsidy even though it may earn a lower revenue in the short run. In the next scenario, consider the case when Didi provides subsidy. Uber, knowing that Didi provides subsidy, will still choose to subsidize because it will earn a lower revenue if it chooses not to. This is because the higher price compared to Didi’s will cause Uber’s customers to turn to Didi. From this, we can see that from Uber’s perspective, the dominant strategy is to subsidize, regardless of Didi’s decision. Since Didi faces the same situation, the same analysis and conclusion can also be applied to Didi. In conclusion, it is illustrated through Game Theory that the decision for Didi and Uber to provide subsidy will bring the best possible outcome for each firm, regardless of the other party’s decision.