Herd Immunity: The Importance of Vaccines
The relatively disease free world we live in is a result of hundreds of years research into vaccines and other disease prevention measures. Edward Jenner created a smallpox vaccine in 1796 from cowpox material and since then, smallpox has been virtually eradicated from the human population. From there, vaccines continued to develop to a point where many of the world’s most infectious and dangerous diseases are but a memory. However, in recent years there have been a number of outbreaks of those very diseases despite our efforts to immunize against them. For example, from December 28, 2014 to February 8th, 2015 there were a total of 125 cases of measles. A good fraction of the patients (35%) visited one or both of California Disney Land theme parks. Why have our efforts to prevent infectious disease failed in recent years? The answer lies in the concept of herd immunity.
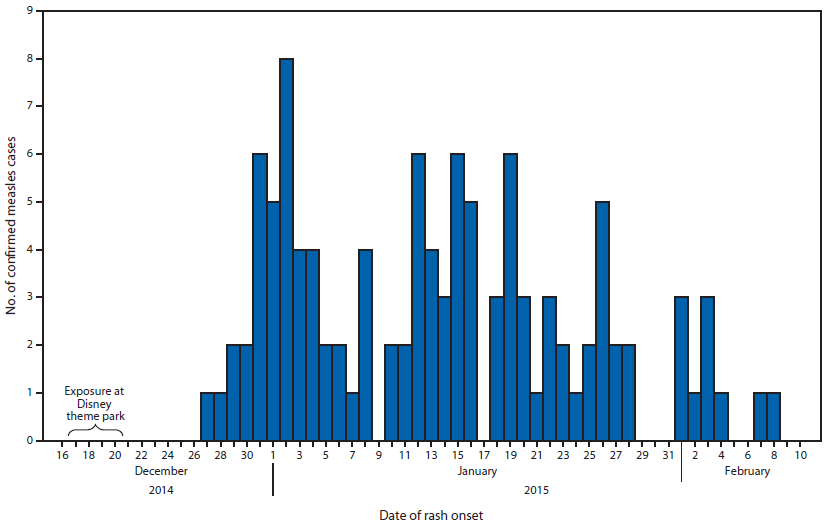
The figure above is a histogram showing the number of confirmed measles cases (N = 110), by date of rash onset in California during December 2014-February 2015.
The concept of herd immunity is essentially when there is a high enough percentage of people immunized against a disease so that it cannot spread uncontrollably. To put this in terms of what we learned during class, Ro after vaccination must be less than 1. The more infectious the disease, the higher the initial Ro before vaccination. The higher the initial Ro, the higher the required percentage of people vaccinated for herd immunity. We can model vaccines as reducing k by a certain factor. If somebody is immunized, they are no longer a person that can be infected, so they are effectively removed from the contact network. 90% vaccination means that k is now 1/10 of its original value, assuming the vaccine works 100% of the time.

Ro Values and threshold vaccination % for herd immunity for some infectious diseases. Image credit: © Tangled Bank Studios; data from Epidemiologic Reviews 1993.
These outbreaks are occurring because we are approaching and sometimes dropping below the threshold percent of herd immunity. In recent years, parents have been avoiding vaccines because of various reasons. One reason is that they can potentially cause autism. This is not the case, as many studies have shown there to be no correlation between the two and the original study claiming the vaccine-autism link turned out to be faked. In addition, vaccines may have worked a little too well, and young adults now don’t really know the potential harm these infectious diseases may bring. In order to prevent outbreaks like these in the future, we must be properly educated on the importance of vaccination.
Herd Immunity: http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/body/herd-immunity.html
History of Vaccines: http://www.historyofvaccines.org/content/timelines/all
California Outbreak: http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm6406a5.htm
