By: Wei Cheng
Funny slides always make your life easier :Introduction of genomics tools(ppt)
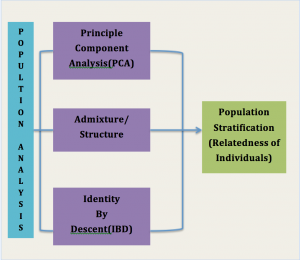
Type of Analysis
- Population Analysis
- Association/Linkage Analysis
Admixture/Structural/Ancestry Analysis & clustering
Microsatellites-Whole-genome-sequencing
Linkage Analysis vs Association Analysis
In the past, neither association tests nor linkage tests were “genome-wide”; it was not feasible or affordable to test the whole genome at constant time. But now as the invention of the SNP chips, that measure hundreds of thousands of loci spread across the whole genome is available. Here comes “GWAS”
Genome-Wide Association Study(GWAS)
Definition
GWAS is an examination of many common genetic variants in different individuals to see if any variant is associated with a trait.1
An example of principles and steps of GWAS.
“Genome-wide association study and ancestral origins of the slick hair coat in tropically adapted cattle”14
The research makes use of GWAS, haplotype analysis, signatures of selection, runs of homozygosity and identity by state calculations to identify a 0.8Mb consensus region for the SLICK locus on BTA 20 in which contains SKP2 and SPEF2 as possible candidate genes.14
**Illumina’s Infinium Beadchips(Data Analysis) & Affymetrix-Genechip
***EMMAX Software and EMMA Algorithm
Reference:
- Wikipedia.
- Eui-Soo Kim and Max F. Rothschild*, Genomic adaptation of admixed dairy cattle in East Africa, Front Genet. 2014; 5: 443. Published online 2014 Dec 19. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00443
- Klein RJ; Zeiss C; Chew EY; Tsai JY et al. (April 2005). “Complement Factor HPolymorphism in Age-Related Macular Degeneration”. Science 308 (5720): 385–99.
- Schena M; Shalon D; Davis RW; Brown PO (October 1995). “Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray”. Science 270 (5235): 467–70.
- Henderson, Matthew P. A .“GWAS”.(01/01/2013) 25.
- Duxue Cheng, “猪肉质性状的全基因组关联研究”.(2012) 19-20.
- Henderson, Matthew P. A .“GWAS”.(01/01/2013) 26.
- Weedon MN, Lettre G, Freathy RM, Lindgren CM, Voight BF, Perry JR, et al. A common variant of HMGA2 is associated with adult and childhood height in the general population. Nat Genet. 2007;39:1245–50.
- Arking DE, Pfeufer A, Post W, Kao WH, Newton-Cheh C, Ikeda M, et al. A common genetic variant in the NOS1 regulator NOS1AP modulates cardiac repolarization. Nat Genet. 2006;38:644–51.
- Henderson, Matthew P. A .“GWAS”.(01/01/2013) 28.
- McPherson R, Pertsemlidis A, Kavaslar N, Stewart A, Roberts R, Cox DR, et al. A common allele on chromosome 9 associated with coronary heart disease. Science. 2007;316:
- Henderson, Matthew P. A .“GWAS”.(01/01/2013) 27.
- Ragoussis J. Genotyping technologies for genetic research. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2009;10:117–33.
- Heather Huson and etc.“Genome-wide association study and ancestral origins of the slick hair coat in tropically adapted cattle” Published online 2014 Apr 29. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00101
- Wigginton JE, Cutler DJ, Abecasis GR. A note on exact tests of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;76:887–93.
- Cox DG, Kraft P. Quantification of the power of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium testing to detect genotyping error. Hum Hered. 2006;61:10–4.
- Price AL, Patterson NJ, Plenge RM, Weinblatt ME, Shadick NA, Reich D, et al. Principal components analysis corrects for stratification in genome-wide association studies. Nat Genet. 2006;38:904–9.
- Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81:559–75.
- Zhang X, Cao ZW, Lin ZX, Wang QK, Li YX.“EMMA: an efficient massive mapping algorithm using improved approximate mapping filtering.” Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2006 Dec;38(12):857-864.
- De Bakker P. I., Yelensky R., Pe’er I., Gabriel S. B., Daly M. J., Altshuler D. (2005). “Efficiency and power in genetic association studies”. Nature Genetics 37 (11): 1217–23
- Turnpenny P, Ellard S (2005). Emery’s Elements of Medical Genetics, 12th. ed. London: Elsevier
- Eric L. Stevens and etc, Inference of Relationships in Population Data Using Identity-by-Descent and Identity-by State, PLoS Genet. 2011 Sep; 7(9): e1002287.