By Doris Byeon
Part I: Songdo I: Why is the ideal city failing?
The development of Songdo became more than just a decentralization of housing; instead, the project reflected the government’s aim for a highly modern, green, and sustainable city.
In fact, Songdo sought to distinguish itself by providing something Seoul could not offer: higher quality living facilities with more sustainable and high modern technology, and its proximity to the international airport. Although Seoul is a modern city, Songdo was one step further in terms of its technology and sustainability.

Combination of high technology and sustainability
“Songdo IBD: South Korea’s New Eco-City | Inhabitat – Sustainable Design Innovation, Eco Architecture, Green Building.” Inhabitat Sustainable Design Innovation Eco Architecture Green Building Songdo IBD South Koreas New EcoCity Comments. Inhabitat. Web. 16 Dec. 2013.
The 100 million square foot master plan, designed by Kohn Pedersen Fox, won the international award and recognition: Financial Times Sustainable Cities Award (2008), and HKIA People’s Choice Award for Urban Design (2007). The master plan includes with an commercial space, residences, retail shops, hotels, and civic/cultural facilities (Master Plan). The Songdo ambitiously implemented high technology clustered development. The 151 Incheon Towers, a sustainable and modern skyscraper (offices, residential space, and a hotel), reflects the scale and technology of the development. Also, Northeast Asia Trade Center (NEATT) is the tallest building and most advanced corporate center in South Korea. Songdo also aims for a development with high sustainability. In fact, Songdo International Business District became one of the Asia’s largest green developments: it surpasses 13 million square ft of LEED certified space. Gale International (developing Songdo City) is targeting for 80% of the buildings certified by LEED. Songdo uses both Korean and international green building rating systems; Songdo has a high standard of sustainable design and construction (Sustainable City).
Furthermore, Songdo has a great ambition for its transportation: accessibility and connectivity of the city. The Incheon’s international airport is already one of the largest airports, and the Incheon Grand Bridge connects Songdo and the airport in 15 minutes. Also, Songdo has great connectivity with Seoul through roads, rails and metros. Songdo development is based on the principles of New Urbanism and implements positive planning aspects into the zoning. It has a large focus on “Smart Growth, Transit Oriented Development, and Green Growth” (Sustainable City). Its ambition to develop a high quality of living and housing gradually led to the development of transportation system as well.
Furthermore, the public housing provides a flexibility of available urban design options for appropriate transitions (Kodmany 95). Commercial towers and variety of architecture enhance flexibility. With much more emphasis on pedestrian-sidewalks, Songdo has taken inspiration from other world-wide famous attractions such as NYC’s Central Park, Parisian Boulevards, or convention center resembling an opera house. Such open and green space is what makes Songdo an ideal city.
Songdo City Central Park and Canal
Building a Skyline
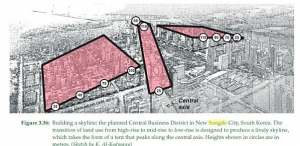
Variety of architectures (high-rise, mid-rise, to low-rise) enhances the flexibility
Kodmany, Kheir, and Mir M. Ali. The future of the city: tall buildings and urban design. Southampton: WIT Press, 2013. Print.
Overall, Songdo stimulated the idea of ‘healthy urban life’. Initial goal for urban sprawl stimulated various aspects of development (economic, business, sustainability), and the government sought to meet demands of the people. Songdo provides the advantage of the new urban development with flexibility and accommodation for better quality living.
Despite its successes and high potential, Songdo is experiencing challenges. More people are perceiving Songdo as a “failed” satellite city. Although it is a mistake to conclude city as a “failure” when it is still on its process of development, it is important to think more critically on the factors that cause that diminishes the city’s development. Despite its ideal and perfect living standard, the development is experiencing several postponements, and there are many vacant residential and retail zones. Whether people will be motivated to move to Songdo in reality is questionable. In fact, people do not simply move their homes just because of the improved ‘sustainability and flexibility’ of the facilities. So, for whom has the government developed such high quality public housing? Other aspects of the city (like its economy or business) should be further examined to see the successes and failures of the city.
References
Kidney, Grant J. “World’s First ‘Smart City’ To Be Completed By 2015: ‘Songdo’ The Orwellian Control Grid.” 29 July 2012. Infowars.com. Web. 23 Oct. 2013.
Kim, Joon H. “Korean Environmental Regulations: Ready to Take on One of the World’s Largest Private Real Estate Development Projects?” Pacific Rim Law & Policy Journal 1 June 2006: 2. Print. (Peer-reviewed)
Shwayri, Sofia T. “A Model Korean Ubiquitous Eco-City? The Politics of Making Songdo.” Journal of Urban Technology 20.1 (2013): 39-55. Print. (Peer-reviewed)
Winden, Willem van. Creating Knowledge Locations in Cities: Innovation and Integration Challenges. London, NY: Routledge, 2012. Print.

